
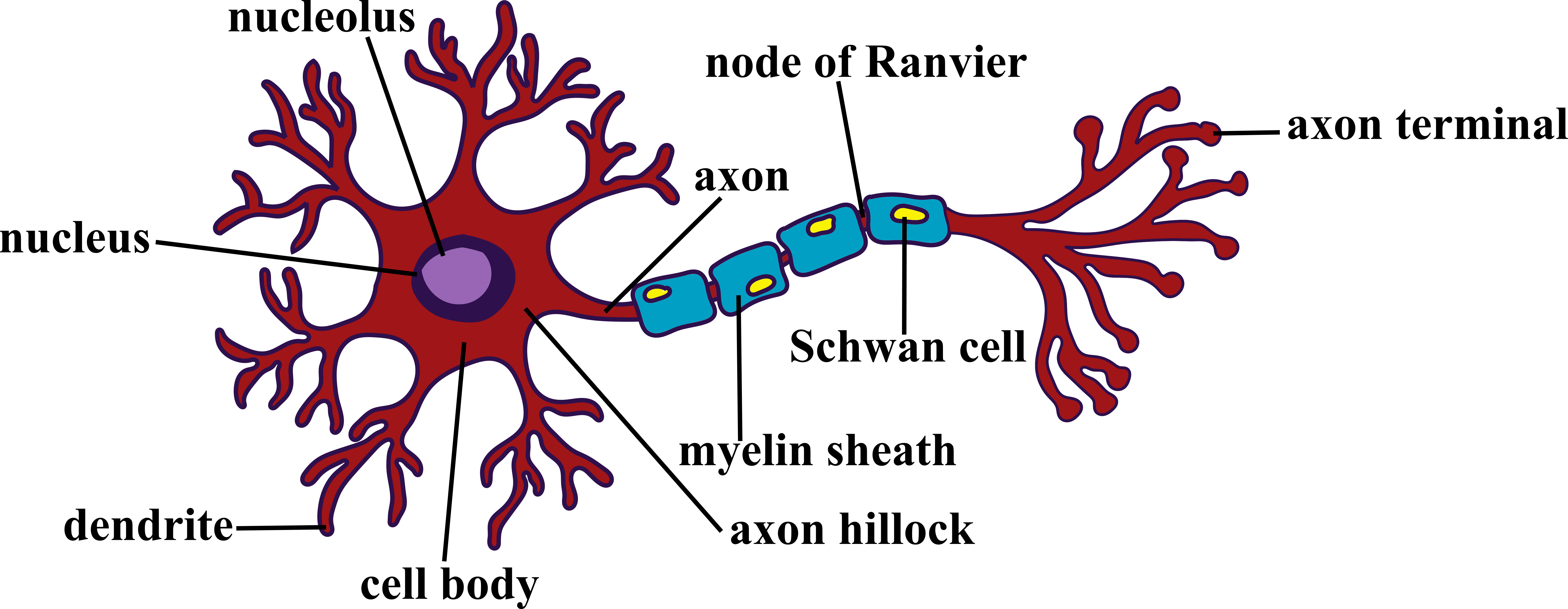
Anatomy Of A Neuron ANATOMY
A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron [1]) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. [2] There are two types of motor neuron.
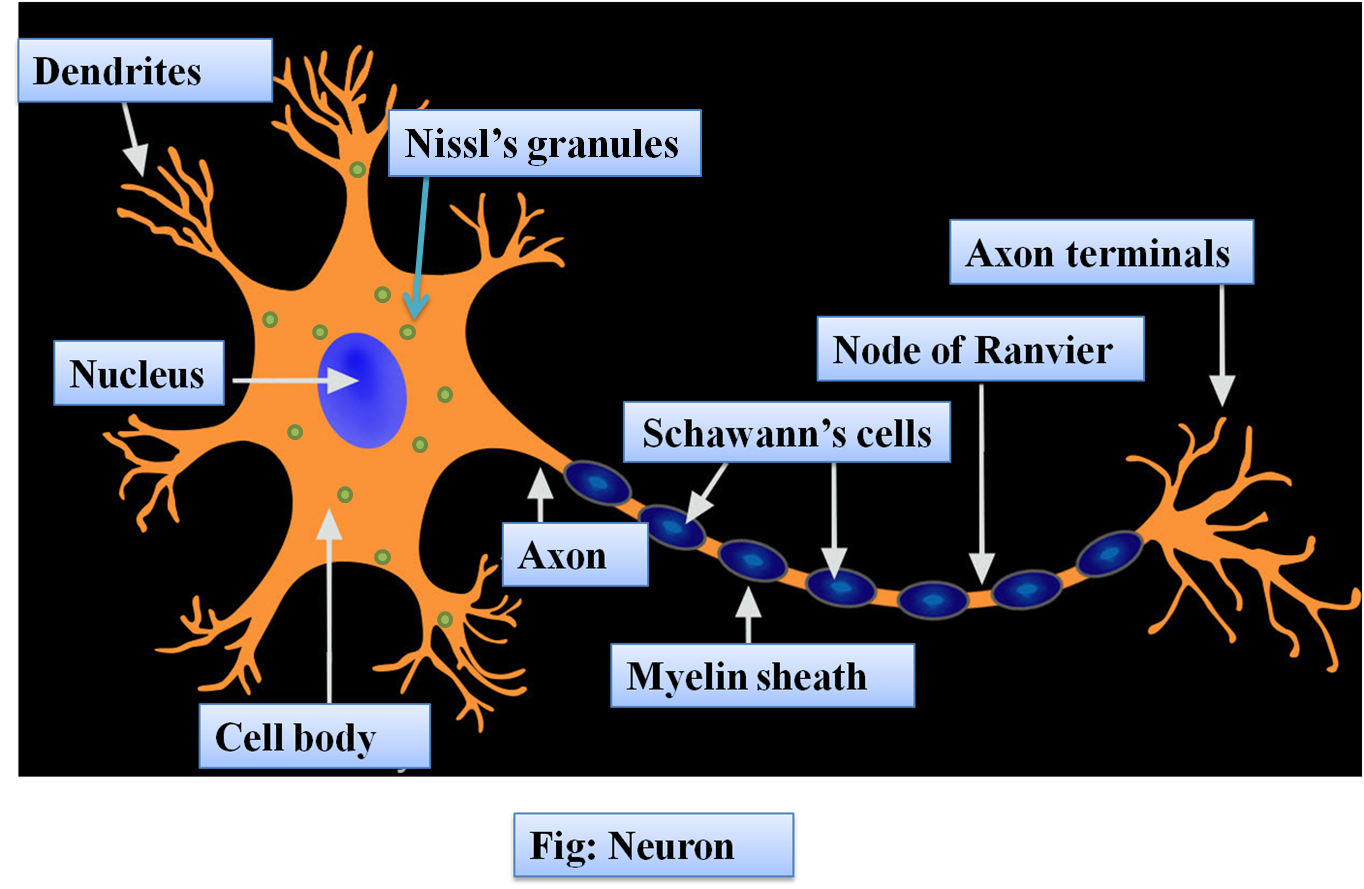
Parts Of A Motor Neuron
By injecting into muscle groups visible tracers that are transported by the axons of the lower motor neurons back to their cell bodies, the lower motor neurons that innervate the body's skeletal muscles can be seen in histological sections of the ventral horns of the spinal cord. Each lower motor neuron innervates muscle fibers within a single muscle, and all the motor neurons innervating a.

Neuron Diagram Straight from a Scientist
Answers for Model #1 Muscle Fiber Model. B. I-band. C. A-band. I. NMJ or neuromuscular junction or synapse between muscle fiber and motor neuron or synaptic cleft. J. Acetylcholine or acetylcholine in synaptic vesicle or synaptic vesicle. M. Schwann cell (specifically this is the nucleus of the Schwann cell)

Figure 7 4 Structure Of A Typical Motor Neuron Bangmuin Image Josh
Sparse labelling and whole-brain imaging are used to reconstruct and classify brain-wide complete morphologies of 1,741 individual neurons in the mouse brain, revealing a dependence on.
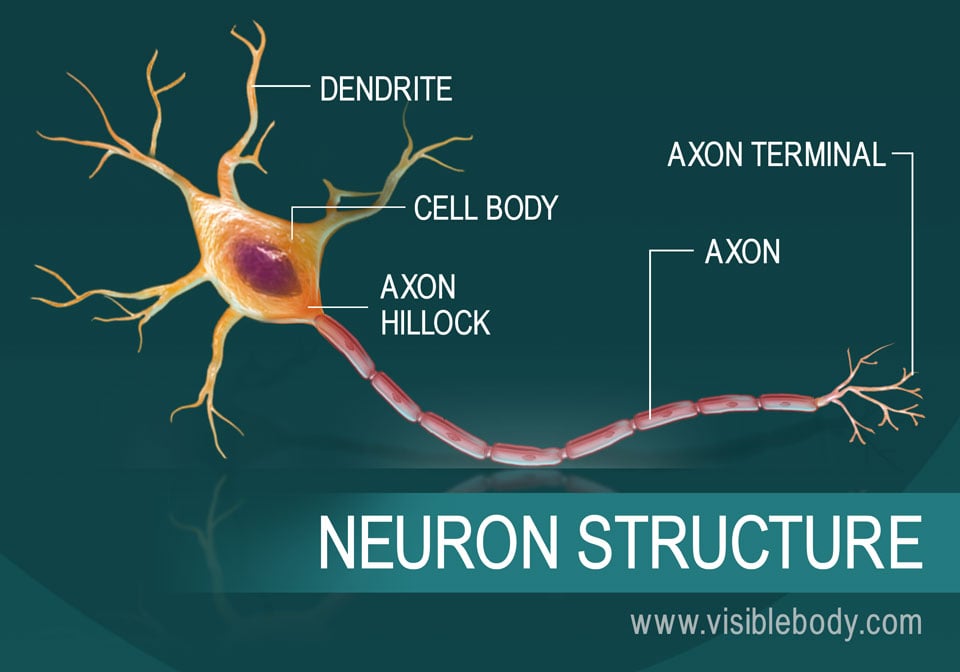
Neurons
First-order spinal motor neuron labeling was restricted to only one motor nuclei (representative images provided in Figure 2A) and observed in the appropriate lumbar segments (approximately L2-L5 for both TA and soleus) with an overlapping rostral to caudal distribution . Labeling of these spinal motor neurons was first noted at 24 h for soleus.

Motor Neuron The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
The understanding of the spatial relationship of different motor neuron pools targeting specific muscles is useful not only for the diagnosis of limb dysfunction caused by motor neuron impairment but also contributes to the development of precise therapy by delivering drugs into a targeted area ( Tosolini and Morris, 2016; Tosolini and Sleigh, 2.
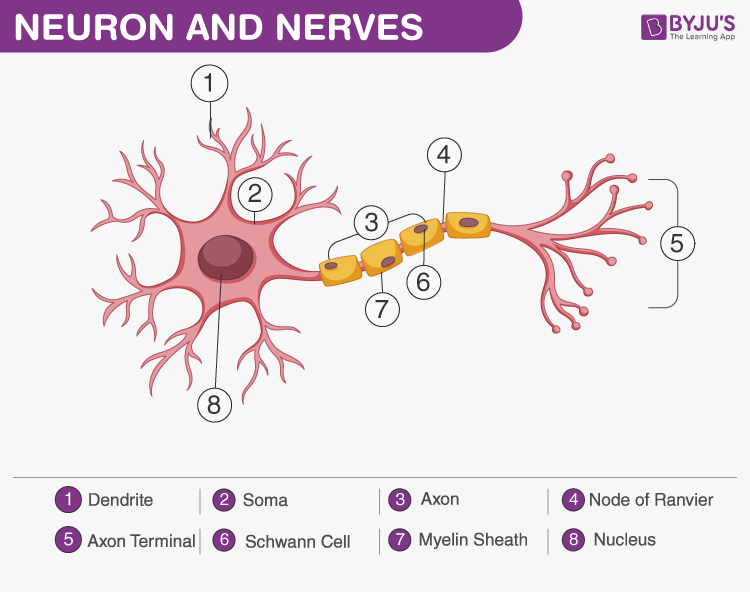
Neuron and Nerves An Overview of Neuron, Nerves and Nervous System
Several factors can lead to variability in motor and sensory neuron counts between and within experiments, including the methods of labeling and counting neurons. We counted motoneurons using 50 μm longitudinal sections of the spinal cord and corrected for double counting using the well-established method previously described by Abercrombie.

Structure of neurones
A motor neuron is a cell of the central nervous system. Motor neurons transmit signals to muscle cells or glands to control their functional output. When these cells are damaged in some way, motor neuron disease can arise. This is characterized by muscle wasting (atrophy) and loss of motor function. Motor Neuron Overview
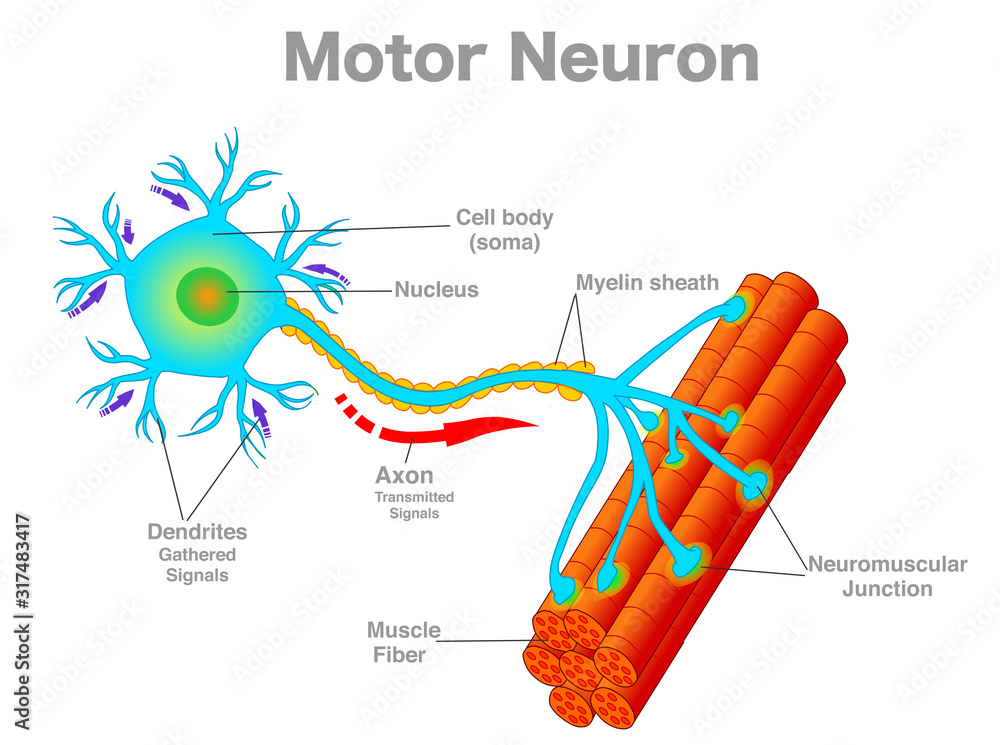
Motor neuron, motoneuron diagram. Transmission of the nerve signal from the neuron to the muscle
Introduction. Motor neurons (MNs) are neuronal cells located in the central nervous system (CNS) controlling a variety of downstream targets. There are two main types of MNs, (i) upper MNs that originate from the cerebral cortex and (ii) lower MNs that are located in the brainstem and spinal cord. Among the latest, spinal MNs (SpMNs) have been.

Nervous system Neurons, Signals, Reflexes Britannica
Most of the RNA in motor neuron cell bodies is ribosomal RNA. In the course of characterizing isolated bovine motor neurons, we found an average RNA content of 1353 ± 37.2 picograms of RNA per cell body ( Capps-Covey and McIlwain, 1975 ). In later, unpublished studies on human lumbar spinal motor neurons, we utilized a more sensitive.

Structure Of A Typical Motor Neuron
NLM NIH HHS USA.gov While the term "motor neuron" evokes the idea that there is only one type of neuron that conducts movement, this is far from the truth.
neural circuit diagram
First, to assess labeling specificity and whether elimination of ephrin-A5 was affecting motor neuron connectivity we examined the position and number of retrogradely labeled motor neurons.

What Are Motor Neuron
Corticospinal motor neurons (CSMN) have a unique ability to receive, integrate, translate, and transmit the cerebral cortex's input toward spinal cord targets and therefore act as a "spokesperson" for the initiation and modulation of voluntary movements that require cortical input.

The Neuron 92F
Motor neurons, also known as efferent neurons, are nerve cells responsible for carrying central nervous system signals towards muscles to cause voluntary or involuntary movement through the innervation of effector muscles and glands. Their nerve fibers are considered to be the longest in the human body .
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neuron-anatomy-58530ffe3df78ce2c34a7350.jpg)
Neuron Anatomy, Nerve Impulses, and Classifications
Fig. 1: A dual-AAV sparse labeling system for tunable labeling of genetically defined neurons and whole-brain single-neuron reconstruction. a , Design of dual-AAV sparse labeling system.
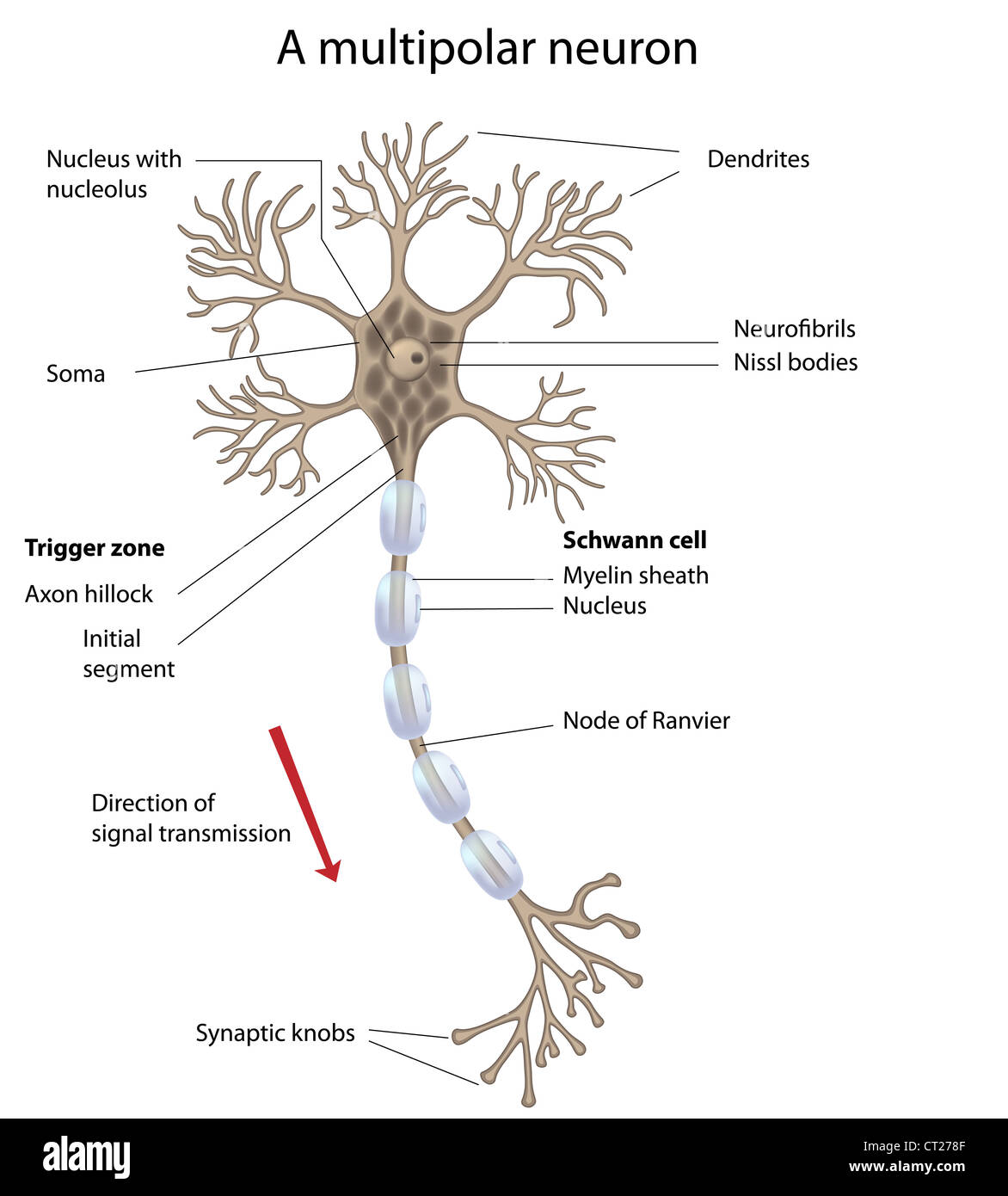
Motor neuron, labeled Stock Photo Alamy
The cell bodies of some PNS neurons, such as the motor neurons that control skeletal muscle (the type of muscle found in your arm or leg), are located in the CNS. These motor neurons have long extensions (axons) that run from the CNS all the way to the muscles they connect with (innervate).